Okay, so if you’re somewhat a beginner in web development, you must’ve heard people telling you that, “You should learn react” or vue or angular, etc.
So, what exactly is it? Should you learn it? If yes, then How to get started? We’ll be discussing answers to all these questions above.
NOTE This post expects you to have some good knowledge about html, css and javascript, especially some important concepts of ES6 or further patch version.
If you don’t feel comfortable with these currently. Then, I am of the opinion that you should first know all these, before jumping on to libraries like React. If you’d like to just quickly freshen up your minds and recall important concepts of ES6, you can read my other post here.
What I’ll be covering in this article?
Before we start, I’d like to point out that I won’t be able to cover, every single thing that is out there to know about react, that’s just not practically possible. I’ll be covering all the basics and some important concepts that can help you to get started with react. But some of the advanced concepts such as redux etc. are beyond the scope of this article.
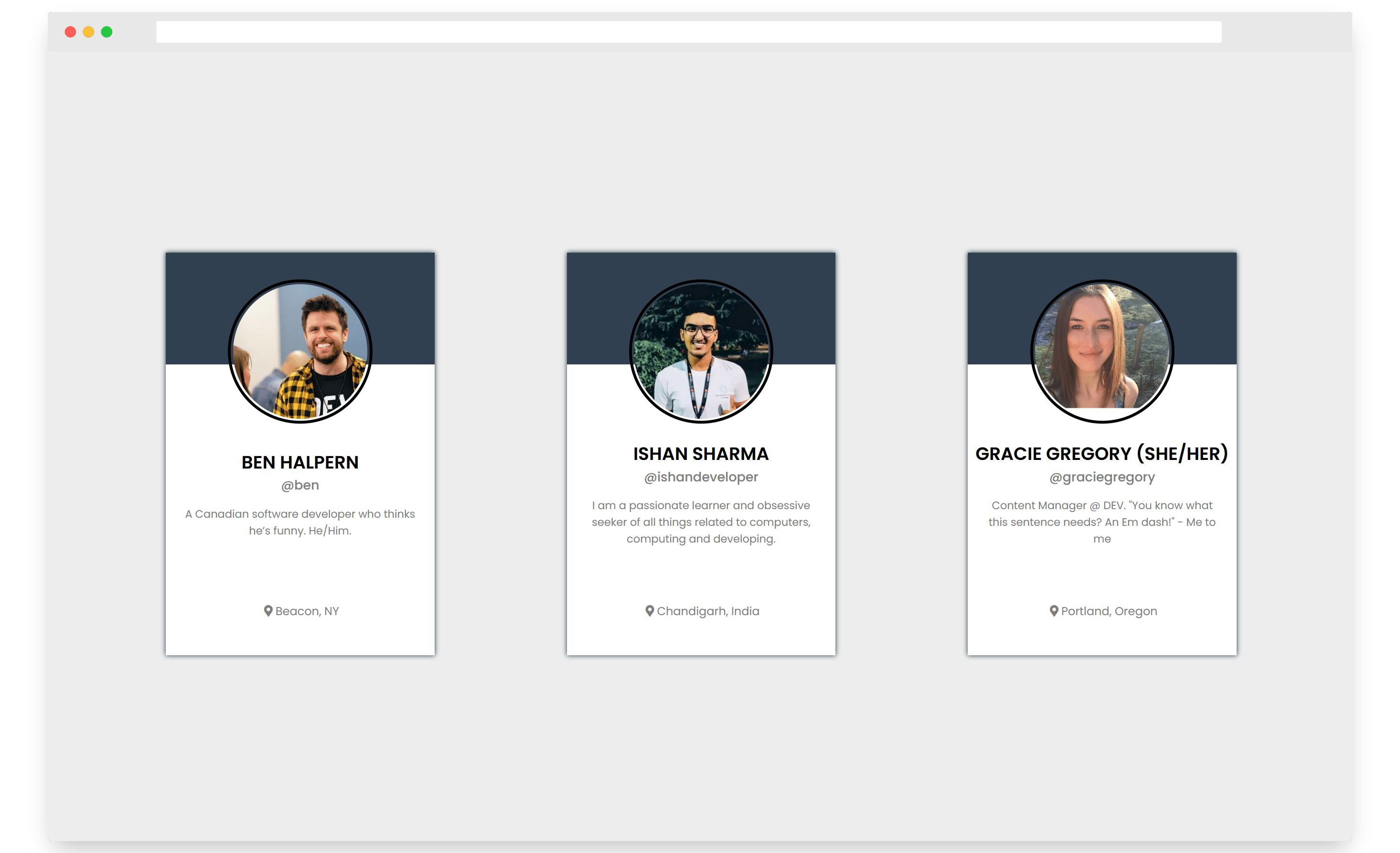
Further in this article, we’d have created a react app, similar to this. In which we’ll just pass a username into the card component, and it’ll fetch the data from dev.to API to create a profile card.
Okay, with all that aside. Let’s jump ahead to learn.
What is React?
and why is everyone so obsessed over it?
React is a JavaScript library built by Facebook. It is used for building front-end user interfaces. The main feature of react is that it makes your UI more modular, by enabling you to divide your interface in smaller components. This model of thinking fits user interfaces well.
React has literally changed the way we think about web applications and user interface development and made it possible to build and manage large-scale web applications such as Facebook, Netflix and many more in a more-efficient and modular way.
How does it work?
Instead of jumping directly, into just learning react, we should first have at least an idea about how it actually works under the hood.
To keep it brief and simple, In layman terms, what react does is that instead of manipulating the web browser’s DOM directly, It creates this Virtual DOM in memory, where it does all these manipulations.
It then examines what changes have been made in the Virtual DOM and then applies those changes in the browser’s DOM.
Let’s discuss about some important concepts.
A. Components
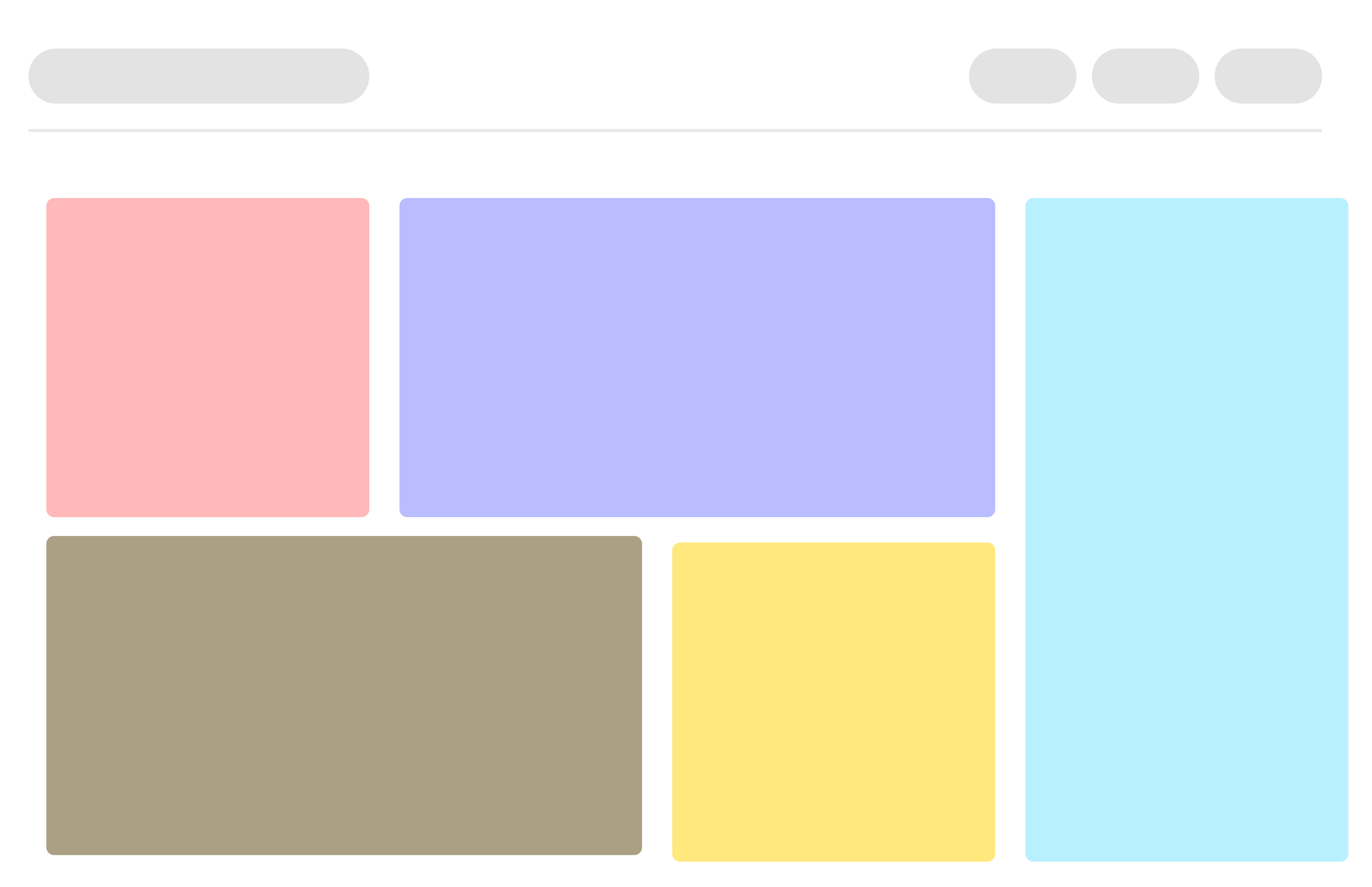
Components are the most fundamental building blocks of a react application. In React, a single web page can be divided into small blocks that represent a different part of the screen. Consider the layout below for an example.
Here every colored box that you can see, represents a different component. Each individual component is independent of one another and responsible both for it’s visual appearances and its interactions.
In layman terms, a component is basically just a file that contains all the html, styling and js logic in one group.
B. JSX
Since React uses JavaScript, you might be wondering, how we’ll be able to create and render elements on the screen. For creating a basic element through vanilla javascript, we usually use
1var header = document.createElement("h1");2header.innerHTML = "Hello World !";
Although this approach is totally okay and we can still use this one in React, but you can imagine, how cluttered our code would look?
Just to give you can example, let’s try creating an unordered list, consisting of three elements, in the casual way.
1const List = () => {2 const alphabets = ["a", "b", "c"];34 return React.createElement(5 "div",6 null,7 React.createElement("h2", null, "Alphabets"),8 React.createElement(9 "ul",10 null,11 alphabets.map((item) => {12 return React.createElement(13 "li",14 { className: "alphabet" },15 item16 );17 })18 )19 );20};
Looks scary for accomplishing such a simple task, right? Now, Let’s try achieving the same in the JSX way.
1const List = () => {2 const alphabets = ["a", "b", "c"];34 return(5 <div>6 <h2>Alphabets</h2>7 <ul>8 {alphabets.map(item=>9 <li className="alphabet">item</li>10 )}11 </ul>12 </div>13 )14}
Noticed the difference? So much less boilerplate and somewhat more elegant code. That’s JSX.
At first sight, you might be thinking, this looks like HTML. You are not alone, every new React developer thinks the same at first. I also thought the same.
But, the funny thing is, it’s not HTML. It is just a syntax extension to JavaScript, or you can say some sugar syntax for defining components and their positioning inside the markup. If you’d like to learn more in depth about JSX, refer to React docs, here.
I believe in learning by doing approach, that’s why for the rest of this tutorial we’ll be exploring react by working on a very basic react project.
C. Component State
If you try to read the react documentation to figure out what state is, it can be quite difficult to grasp at first. This is why usually many of the beginner tutorials out there, tend not to cover this concept. But in my opinion, it’s not that complicated and super simple to grasp and I believe it’s a very important concept to learn for everyone who’s trying to learn react.
You can imagine state of a component as the output of that component on the basis of some particular data, or a variable let’s suppose. For example, In case of an hour clock, the output of the component must change after every single hour let’s say from 1 AM to 2 AM. So, the output of that clock component at 1 AM, can be referred to as a state of that component.
Or another example, In case someone tries to visit your website and you want to display a login page to the visitor, in case they aren’t logged in and display a dashboard instead, when they are logged in. Here the boolean condition whether a user is logged in or not can be referred to as state of that component.
It’s important to remember that whenever the state of a component changes, the component will re-render itself. For example, once a user has logged in we’d want to take him to the dashboard, instead of the login page.
We’ll be seeing this in action, while we’re working on our project.
1. Setting up our react project.
For testing purposes, we can quickly get set up with React by just including three scripts in our index.html file.
a. Using Global Scripts
1<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>2<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>3<script src="https://unpkg.com/babel-standalone@6.15.0/babel.min.js"></script>
If you’d like to go with that approach, you can absolutely do that and still be able to follow along in this tutorial. But, In production environments, we prefer to use a few build tools since React tends to utilize some functionalities which won’t work by default in browser.
For this tutorial, I'll be going with the latter approach, and actually setting up a production react environment.
But, If you’ve decided to go with the previous one, just please create an ‘app.js’ file in the same directory and make sure that your ‘index.html’ file looks similar to this.
1<!DOCTYPE html>2<html>3 <script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>4 <script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>5 <script src="https://unpkg.com/babel-standalone@6.15.0/babel.min.js"></script>6 <body>78 <div id="root"></div>910 <script type="text/babel" src="./app.js"></script>11 </body>12</html>
b. Using Build Tools
For those, who’re going the previous approach can skip this part but for those who’d like to set up a react environment can follow along.
Ensure that you’ve node.js installed on your system. You can check this by running
node -vin your terminal.If you get an output with a version number xx.xx.x . Then, you’re good to go!
But, if you get some error like command not recognized, then please download and install node.js installer package from here.Create a new react project Once you’re set up with node. Open your terminal and
cdinto your desired directory. Now, you can run this command to install create-react-app globally on your system using npm (node package manager).1npm install -g create-react-appIt may take a few seconds, depending upon your internet connection.
Now, we can finally create our react project. It’s pretty simple. You can just run.
1npx create-react-app todoThis may take a while. Once that’s done, you can just cd into the app folder and run the app locally using
1cd todo2npm startIt’ll open up a browser window, and you should be able to see something like this

Congratulations, you’ve just created created your first react project! 🎊
We’ll go through everything that’s happening in the code and folder structure in just a minute, but first let’s clear up some unwanted clutter.
To speed things up, you can download these starter files from here and copy replace the src folder. If you’ve done this, then you can just run
npm start, skip the latter part and jump to Understanding the project structure.If you’d still prefer to do things manually instead,
Inside the ‘src’ folder, you must be able to see a lot of files. Let’s start by cleaning these. Let’s delete the all other files in src folder, till you’re left with just these 3, ‘App.js’, ‘index.js’, ‘index.css’.
You must be getting an error in your terminal. Let’s fix this.
Open the ‘index.js’ file and remove all deleted imports, and serviceworker code. Till you’re left with something similar to this
1import React from "react";2import ReactDOM from "react-dom";34import "./index.css";5import App from "./App";67ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));Still facing an error? Let’s open up the ‘App.js’ file.
Remove the import logo and app.css lines and replace the return statement with a h1 header. Your ‘App.js’ file should look like this
1import React from "react";23function App() {4 return <h1>Hello World</h1>;5}67export default App;Finally, open the index.css file, select all and delete its content.
Make sure that you’re still running the npm start command. Now you should be able to see ‘Hello World’ in your browser window.
2. Understanding the project structure.
Let’s open up our project folder in explorer or finder and you’ll notice the first thing that we have is
‘node_modules’. ‘node_modules’ simply contain all the different packages that we’ve installed using npm. We don’t ever touch this folder very often, and you can ignore it.
A tip to keep in mind is that, we never commit node_modules folder in version control, as they can be generated on the host machine by running
npm install.‘public’ contains our index.html file, icon and a manifest file(which you can just ignore for now).
‘package.json’ This file holds some scripts and name of some packages, that basically start our react project. It’s just a file created by the npm.
‘src’ most of our work is going to be in this folder.
Let’s open the App.js.
Here in our App.js file, ‘App’ is a component. This particular implemenation is called functional component. We write a function exactly similar to how we define a function in vanilla javascript.
function App(){}
How it differs from vanilla javascript is that instead of returning a value, it returns a component, like
1function App(){2 return (3 <h1>Hello World</h1>4 )5}
We can also write the same in a single line, using arrow functions.
1const App = ()=> <h1>Hello World</h1>
Now, because we want to use this component in other pages, we need to export it by using
export default App
Let’s jump back to our ‘index.js’ file and see how this component is being used.
You can see in the index.js file, what happens is we’re again importing react, along with ReactDOM.
Then, we’re using a method ReactDOM.render method to render our ‘App’ Component, followed by a comma and document.getElementById('root').
Okay, so what’s happening here? What happens is, that when we use ReactDOM.render method, we ask it to render the App Component, by injecting it inside the element having an id of ‘root’. What react does is it takes all our javascript code and generates the desired html from that.
You can verify this by opening the index.html file in the public folder. You must be able to see this <div id="root"></div> in the body tag.
3. Creating Dev Cards
Let’s break down our initial idea of the app, showcasing three users into components. We can easily observe that the layout of these profile cards is quite similar in all three cases, except for the data enclosed in-between.

Let’s first focus on building an html layout for this component. For the sake of simplicity, I’ve already included all the css required for this project in index.css in the starter files.
In case, you didn’t download the starter files and went for the manual approach, just copy-paste the css from below into your index.css file.
1@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Poppins:wght@400;500;600&display=swap");2@import url("https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/5.14.0/css/all.min.css");34* {5 box-sizing: content-box;6 margin: 0;7 padding: 0;8 font-family: "Poppins", sans-serif;9}10:root {11 --main-color: #eee;12 --dark-color: #2c3e50;13 --text-color: #7f7f7f;14}15.wrapper {16 min-height: 100vh;17 background: var(--main-color);18 display: flex;19 justify-content: center;20 align-items: center;21 justify-content: space-evenly;22 flex-wrap: wrap;23}2425.card {26 width: 300px;27 height: 450px;28 background: white;29 margin: 1rem;30 display: flex;31 flex-direction: column;32 justify-content: space-between;33 box-shadow: 0px 0px 5px #233942;34}3536.card img {37 background: var(--main-color);38 margin-top: 30px;39 border-radius: 50%;40 position: absolute;41 width: 150px;42 height: 150px;43 padding: 0.15rem;44 border: 0.2rem solid black;45}46.user-image {47 position: relative;48 width: 100%;49 height: 200px;50 display: flex;51 justify-content: center;52}53.user-image:before {54 content: "";55 height: 125px;56 width: 100%;5758 background: var(--dark-color);59}60.user-info {61 display: flex;62 flex-direction: column;63 align-items: center;64}65.user-info .name {66 font-size: 1.25rem;67 text-transform: uppercase;68 font-weight: 600;69}70.user-info .handle {71 font-size: 0.9rem;72 font-weight: 500;73 color: var(--text-color);74}75.user-info .summary {76 padding: 0.75rem 1rem;77 text-align: center;78 font-size: 0.75rem;79 font-weight: 400;80 color: var(--text-color);81}82.location {83 text-align: center;84 font-weight: 400;85 font-size: 0.8rem;86 color: var(--text-color);87 padding: 2.5rem 0;88}8990.location::before {91 font-family: "Font Awesome 5 Free";92 font-weight: 900;93 content: "\f3c5";94 padding: 0 0.2rem;95}
Inside the src folder, let’s create a new file card.js. Here, we’ll be creating our card component.
Let’s start by importing react and writing boilerplate function for our card.
1import React from "react";23function Card() {4 return(5 <h1>This is a Card</h1>6 )7}89export default Card;
Let’s save the changes and open our browser to see the results. Wait, it’s not showing up? That’s because we haven’t imported this in our App component.
To fix this, let’ open our App.js file and replace the <h1>Hello World</h1> with
1import React from "react";2import Card from "./card";34function App(){5 return (6 <div class="wrapper">7 <Card />8 </div>9 );10}1112export default App;
Now you should be able to see, something like this in your browser

Although, this works, but if you open up your console (Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + J - Chrome, Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + K - FireFox). You must see a warning similar to this
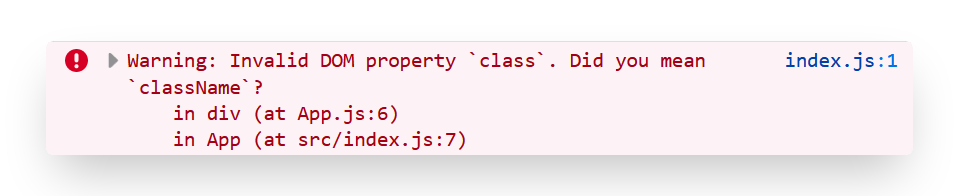
Why are we getting this warning message?
This is because if you look closely in the App function, the div that we’re returning has a class of wrapper. Although, this is the exact way how we define a class in html, but remember I mentioned earlier, this is not html but JSX ?
Because, JavaScript already has a class keyword used for a constructor, that’s why we can’t use class here, to fix this React came up with className. We can fix this by replacing our class with className like this
1import React from "react";2import Card from "./card";34function App(){5 return (6 <div className="wrapper">7 <Card />8 </div>9 );10}1112export default App;
Once you do that, any warnings in the console would get resolved.
With that aside, let’s jump back to our card.js file and build our html layout. I’ve already created a layout with the same classes that were used in our css to speed things up a little bit.
1function Card() {2 return (3 <div className="card">4 <div className="user-image">5 <img src="user.png" alt="User Profile"></img>6 </div>78 <div className="user-info">9 <div className="name">John Doe</div>10 <div className="handle">@johndoe</div>11 <div className="summary">12 Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.13 </div>14 </div>15 <div className="location">New York</div>16 </div>17 );18}
Once you save the changes, you should be able to see something like this in your browser.
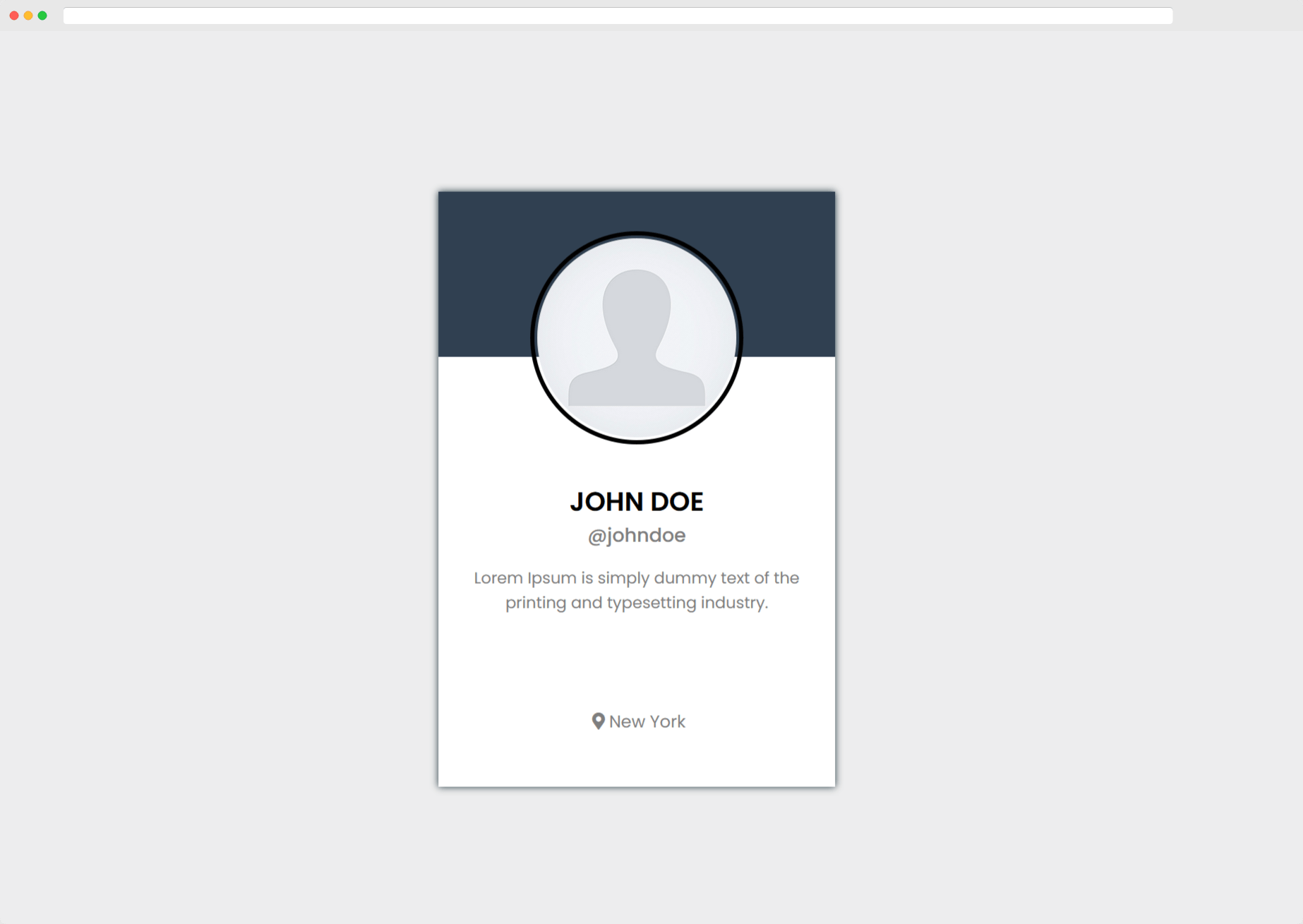
Congratulations for making this far! Our app is finally taking it’s shape. But this is all just static data, right? We want to showcase actual user data instead, on the basis of username.
For that we can use the built in Fetch API method in javascript to retrieve dev.to user’s data from this endpoint : https://dev.to/api/users/by_username?url=bob . Replacing bob with your username. This endpoint sends a json data with the below structure, that we can then parse and display in our component.
1{2 "type_of": "user",3 "id": 1234,4 "username": "bob",5 "name": "bob",6 "summary": "Hello, world",7 "twitter_username": "bob",8 "github_username": "bob",9 "website_url": null,10 "location": "New York",11 "joined_at": "Jan 1, 2017",12 "profile_image": "https://res.cloudinary.com/...jpeg"13}
The simplest way to use fetch API in javascript is to use it like this
1let username="ishandeveloper"; // You can write your username here23fetch(`https://dev.to/api/users/by_username?url=${username}`)4 .then((res) => res.json())5 .then((data) => data);
But, how can we use this in our react app and we want to make sure to call this fetch method, only when a component is mounted/injected in the app tree. To do this, we’ll have to use something called hooks.
Hooks are basically just some functions, that let us to fire up a callback, in certain events of our component. You can read more on that here.
For our goal, we’ll be using the useState and useEffect hook.
a. useState() hook allows one to declare a state variable inside a function.
b. useEffect() hook allows functional components to manipulate DOM elements by executing a callback before each render.
Before we use any of them, we should import them from the react module, by replacing the import React from 'react' with
1import React, {useState, useEffect} from 'react';
So, let’s write our function for fetching the data from API. We’ll use useEffect hook to call a function that fetches the data.
We can simply do this by writing a callback function like this, before the return statement inside the functional component.
1let user={};23useEffect(() => {45 async function fetchData() {6 let username="ishandeveloper"; // You can write your username here78 // Retrieves json data from DEV API9 let dev_data = await fetch(`https://dev.to/api/users/by_username?url=${username}`)10 .then((res) => res.json())11 .then((data) => data);1213 user=dev_data; // Sets the user data14 }1516 fetchData(); // Calls the above function17}, [] );
In the above code, we’re passing a callback function in the useEffect hook, and creating another async function fetchData() inside that callback and calling that async function. This is because, using async directly in the useEffect function is not permitted.
You may also notice that we’re passing an empty array ([]) as a second parameter to the useEffect. Why is that? That is because, by default the
useEffect callback is run every time when a component is either mounted or updated.
So, what’s the issue then? Here’s the catch. Using this approach, we get stuck in kind of a nastly loop. Because we’re fetching the data when the component is mounted and then updating the data, on updating the data the component again re-renders, firing the useEffect callback, and hence we’re stuck in a forever loop.
To fix this, we pass an array as a second argument, to avoid activating it on component updates. You can read more on this in the docs, by scrolling down to the last highlighted note here.
Although, it may seem like everything should work as expected, but the above code won’t re-render the component, that is because we’re not changing the state of the component. We need to explicitly tell react that the state of a component is changed. To achieve this, we we’ll need to use the useState hook.
We can use it to store our user data like this
1const [user, setUser] = useState({});
Let’s break this down
inside the useState method, we can add the initial value of the user variable, that we’d like to store, it can be an object, array, boolean, string, number anything.
The useState method, returns an array of two things, first is the value of the variable itself and second is a callback function that can be used to change the value of that variable.
So, instead of using user=dev_data in our above code, we’d call the setUser method inside the useEffect to update the user data. With these two changes, our above code would become
1const [user, setUser] = useState({});23useEffect(() => {45 async function fetchData() {6 let username="ishandeveloper"; // You can write your username here78 // Retrieves json data from DEV API9 let dev_data = await fetch(`https://dev.to/api/users/by_username?url=${username}`)10 .then((res) => res.json())11 .then((data) => data);1213 setUser(dev_data); // Sets the user data14 }1516 fetchData(); // Calls the above function17}, [] );
Perfect, we’re almost done! 🎊
Now that we have the data, let’s pass it into our JSX code. In JSX, whenever we want to use JavaScript code inside the html looking tags, we enclose that javascript code with curly brackets {}.
On the basis of properties sent by the API Endpoint (mentioned above), here’s how we can format that data in our jsx code.
1return (2 <div className="card">3 <div className="user-image">4 <img src={user.profile_image} alt="User Profile"></img>5 </div>67 <div className="user-info">8 <div className="name">{user.name}</div>9 <div className="handle">@{user.username}</div>10 <div className="summary">{user.summary}</div>11 </div>1213 <div className="location">{user.location}</div>14 </div>15);
With this, your entire code in card.js should look like this
1import React, {useState, useEffect} from 'react';23function Card() {45 const [user, setUser] = useState({});67 useEffect(() => {89 async function fetchData() {10 let username="ishandeveloper"; // You can write your username here1112 let dev_data = await fetch(`https://dev.to/api/users/by_username?url=${username}`)13 .then((res) => res.json())14 .then((data) => data);15 setUser(dev_data);16 }17 fetchData();18}, [] );19202122return (23 <div className="card">24 <div className="user-image">25 <img src={user.profile_image} alt="User Profile"></img>26 </div>2728 <div className="user-info">29 <div className="name">{user.name}</div>30 <div className="handle">@{user.username}</div>31 <div className="summary">{user.summary}</div>32 </div>3334 <div className="location">{user.location}</div>35 </div>36);37}3839export default Card;
With this done, you should be able to see something similar to this in your browser.
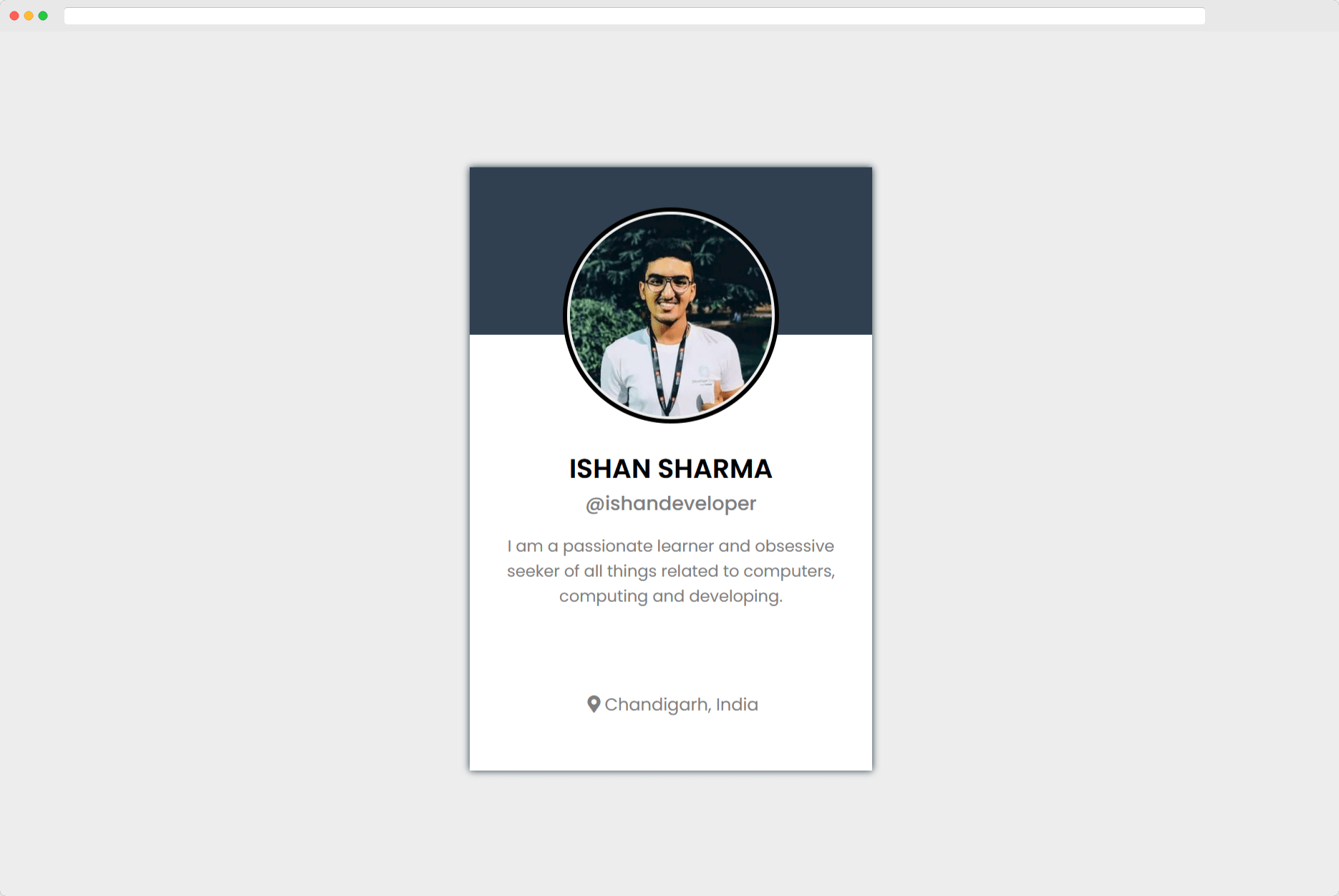
Congratulations and be proud of yourself for making this far! You really deserve a pat on the back 🤙
But we’re not done yet.
4. Re-Using Components
This is what I consider to be one of the best things about React. Remember? Our initial goal was to create something similar to this.

In the above visualization, we’ve three cards showcasing three different profiles instead of one. So, how can we do that? It’s pretty simple actually.
Let’s open our App.js file. Here’s how it looks like currently, right?
1import React from "react";2import Card from "./card";34function App(){5return (6 <div class="wrapper">7 <Card />8 </div>9);10}1112export default App;
You can observe that we’ve written a <Card /> tag here to create a Card Component. We can just duplicate this, twice to get 3 instances of this card Component.
Additionally we can also pass custom properties in this tag markup, these are called props, let’s pass the usernames of different DEV users as username attribute.
1import React from "react";2import Card from "./card";34function App(){5 return (6 <div class="wrapper">7 <Card username="ben"/>8 <Card username="ishandeveloper"/>9 <Card username="graciegregory"/>10 </div>11 );12}1314export default App;
Hit save, and let’s see the changes in our browser.
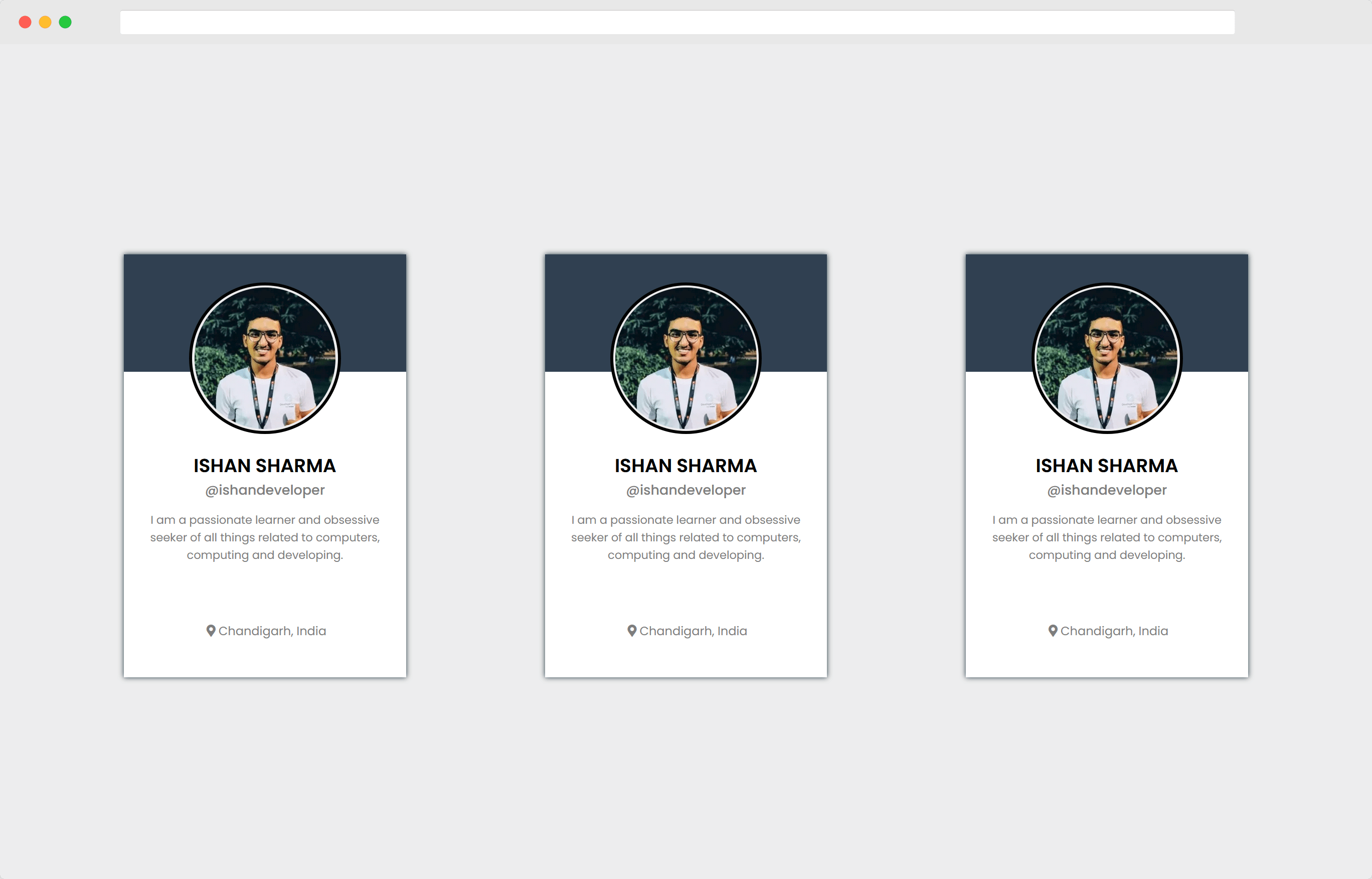
Wait, Something’s weird.
Don’t all of these look the same?
Yes, they do. Because although we’ve passed a username attribute in our cards, we’re not using it.
Let’s fix this. Open up card.js file in your editor.
- The first thing that we’ll need to do is accept those
usernameprops in our functional component.
Let’s do that by adding a props parameter in the function. So that our function becomes like this
1function Card(props) {2 ...........3}
Now we’ll need to replace our hard-coded username with this username prop. It’s pretty easy, just replace the let username="ishandeveloper" with let username=props.username
1useEffect(() => {23 async function fetchData() {4 let username=props.username;5 ...........
Hit save, and that’s it. You’ve successfully completed the whole project! 🎊
Here’s the whole source code for card.js
in case you need it
1import React, {useState, useEffect} from 'react';23function Card(props) {45 const [user, setUser] = useState({});67 useEffect(() => {89 async function fetchData() {10 let username=props.username; // You can write your username here1112 let dev_data = await fetch(`https://dev.to/api/users/by_username?url=${username}`)13 .then((res) => res.json())14 .then((data) => data);15 setUser(dev_data);16 }17 fetchData();18}, [] );19202122return (23 <div className="card">24 <div className="user-image">25 <img src={user.profile_image} alt="User Profile"></img>26 </div>2728 <div className="user-info">29 <div className="name">{user.name}</div>30 <div className="handle">@{user.username}</div>31 <div className="summary">{user.summary}</div>32 </div>3334 <div className="location">{user.location}</div>35 </div>36);37}3839export default Card;
If you’d like to download the project files, or see a live demo of the project, click here.
This was all about this tutorial, I hope this helped you to grasp onto some of the basic and most important aspects of react that can help you to get started easily.
We can discuss more on somewhat advanced topics such as Redux, Context API etc. in futher articles. I hope you enjoyed this one and any feedback we’d be highly appreciated.